A Hands-On, Practical Guide to Programmatic SEO
If you want to make a name for yourself online, brand exposure is the first step. Programmatic SEO is an incredibly powerful tool to help you achieve this. But before you roll up your sleeves and dive in, let's clarify: what exactly is SEO? And how does programmatic SEO work?
Simply put, SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the practice of getting your web pages to rank higher on search engine results pages (like Google) when users search for relevant content. The higher you rank, the more likely users are to click on your site, which brings in traffic.
Why is ranking so important? Take a look at this chart (it's a few years old, but the principle is universal): the top few organic results (not ads) get the vast majority of clicks.
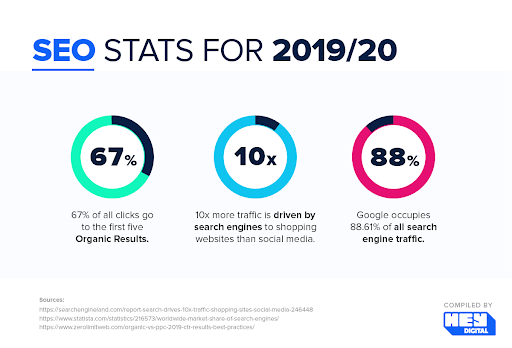
Source: Vixen Digital
So, SEO is fundamental for driving traffic. But what does "programmatic" mean, and how can it help you level up your SEO game?
The Core Goal of This Guide: To give you a systematic understanding of how to implement programmatic SEO, avoid common pitfalls, and provide a step-by-step guide to putting it into practice.
1. First, Let's Understand: What is Programmatic SEO?
Programmatic SEO is not about "black hat" tactics or creating spammy, low-quality sites (though many people might try that, it's a surefire way to get penalized). Its core principle is using technology (code, scripts, tools) to strategically create a large number of valuable web pages at scale, precisely targeting the vast and varied long-tail search queries from users.
For example:
- Travel industry: Batch-generating pages like "family-friendly weekend trips in [City]" or "best budget hotels near [Landmark]."
- E-commerce: Creating pages for "best phone cases for [Phone Model]" or "[Brand] running shoe reviews."
- Education: Generating pages like "best Python tutorials for beginners" or "download past [Exam Name] English papers."
The key is "at scale" + "valuable." If you only focus on quantity and the content is garbage, users won't be satisfied, and search engines will be even less impressed.
A Word of Caution: There are many "bulk website builders" or services out there that claim to generate thousands of pages for you in a day. 99% of them are scams. The content is usually scraped and stitched together, and the user experience is terrible. You'll either get penalized by search engines or end up with a bunch of zombie pages that no one ever sees.
2. Why Bother with Programmatic SEO? What Are the Benefits?
Now that you know what it is, let's look at why it's worth your time and effort:
- Traffic Harvesting Machine (Especially for Long-Tail Keywords): With the right direction and a solid strategy, programmatic SEO can help you cover a massive number of long-tail keywords in a short amount of time. While the search volume for individual keywords might be low, the total volume is huge, and the user intent is highly specific. Our team worked on an auto parts project for a client, and by batch-generating pages for "[Brand] + [Model] + [Part Name]," we increased their website traffic by 5x in six months!
- Cost and Efficiency Powerhouse: Imagine creating thousands or even tens of thousands of pages manually. How much time and manpower would that take? With a programmatic approach, your tech team builds the framework, and your content team provides the "soul," boosting efficiency exponentially.
- Build a Competitive Moat: When you accumulate a large amount of structured content and data through programmatic SEO, your website becomes a formidable content barrier in your niche, building user loyalty and making it very difficult for competitors to catch up.
3. Which Industries/Scenarios Are a Good Fit for Programmatic SEO?
Is programmatic SEO suitable for every website? Of course not.
The best-fit scenarios typically have these characteristics:
- A high volume of long-tail search queries: Users search for things using a wide variety of very specific terms.
- Structured information/data: The content can be organized according to a consistent template and logic, like "[City] + [Service]," "[Brand] + [Model]," or "[Question] + [Answer]."
- Relatively infrequent content updates (or updates can be automated): Otherwise, the maintenance costs are too high.
Commonly applicable industries:
- Travel/Ticketing: [City] + [Attraction]/[Hotel]/[Flight]/[Train Ticket]
- Real Estate: [City] + [Neighborhood] + [Apartment Type]/[For Rent]/[For Sale]
- E-commerce: [Category] + [Brand] + [Model] + [Attribute]/[Price]/[Reviews]
- Recruitment: [City] + [Job Title] + [Industry]/[Salary]
- Education: [Course] + [Institution]/[Instructor]/[Price]/[Rating]
- Automotive: [Brand] + [Model] + [Specs]/[Price]/[Reviews]
- Health & Wellness: [Condition] + [Symptom]/[Hospital]/[Doctor]/[Medication]
- B2B: [Product] + [Model]/[Manufacturer]/[Price]/[Application]
- Local Services/Reviews: [City] + [Service Type] (e.g., Restaurant, Plumber) + [Area]/[Specialty]
International Case Studies (For inspiration, not imitation): Tripadvisor (travel) and Yelp (reviews) are classic examples of programmatic SEO done right. You can study their page structures and content organization, but remember that the market is different, so you can't just copy them directly.
4. A Step-by-Step Guide to Programmatic SEO (Hands-On Tutorial)
Alright, enough with the theory. Here's the main event: how to actually do programmatic SEO, step by step.
Step 1: Keyword Research and Demand Analysis (Build a Strong Foundation)
This is the foundation of all SEO work, and it's even more critical for programmatic SEO.
- Identify Core "Entities" and "Attributes":
- What is the core of your business? Is it "cities," "products," "courses," or "job titles"? These are your "entities."
- What aspects of these entities do users care about? Is it "price," "reviews," "guides," "best," or "near me"? These are your "attributes" or "modifiers."
- Mine for a Massive Number of Long-Tail Keywords:
- Use tools: Common tools include Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, SEMrush, and AnswerThePublic.
- Analyze search suggestions and related searches: The autocomplete suggestions and "related searches" at the bottom of the search results on platforms like Google, Amazon, and Quora are goldmines of real user queries.
- Study your competitors: Use tools to analyze which long-tail keywords your top-ranking competitors are targeting.
- Leverage your own business data: If you have internal search data, customer service logs, etc., make sure to use them.
- Categorize and Filter: Group the keywords you've found (by intent, entity, attribute), and filter out any that are irrelevant, have extremely low search volume, or lack commercial value.
Deliverable: A well-structured and comprehensive keyword database, along with a deep understanding of your users' core needs.
Pro Tip: Don't just focus on high-volume keywords. The total volume and conversion rate of long-tail keywords are often astonishing. Keyword research is not a one-time task; it should be an ongoing process.
Step 2: Competitor Analysis and Strategy Development (Know Thyself, Know Thy Enemy)
Understanding how your competitors are playing the game will help you find your opening.
- Identify Your Core Competitors: Find the websites that rank high for your target keywords and have a similar business model.
- Analyze Competitor Page Structures and Content Templates:
- How do they organize information? What types of pages do they use (list pages, detail pages, category pages)?
- What do their page templates look like? What content modules do they include (text, images, videos, maps, user reviews, ratings)?
- What is the quality of their content? Is it original, repurposed, or scraped? Do they offer any unique value?
- Analyze Their Technical Implementation: Is their URL structure clean? How is their site speed? What about their mobile experience?
- Look for Opportunities for Differentiation: What are your competitors not doing well? What user needs are not being met? What unique value can you offer?
Recommended Tools: Ahrefs, SEMrush, SimilarWeb (for analyzing traffic sources and user behavior).
Deliverable: A clear analysis of your competitors' strengths and weaknesses, and an initial strategic direction for your programmatic SEO efforts (e.g., will you focus on more comprehensive content, faster speed, or a more unique interactive experience?).
Step 3: Page Template Design and Content Planning (Building the Skeleton and Adding the Flesh)
This is the core of programmatic SEO, determining the quality and user experience of your final pages.
- Design Page Templates:
- Based on user needs and competitor analysis, design a page template with a clear information hierarchy that meets the core needs of your users.
- Key Elements: Title (containing the core keyword and click-worthy elements), breadcrumbs, main content area (with a mix of text, images, and clear headings), related recommendations, user reviews/Q&A module, a clear Call-to-Action (CTA), etc.
- Think about differentiation: Your templates should be flexible enough to accommodate unique content, avoiding a situation where all your pages look identical.
- Plan Content Sources and Generation Rules:
- Structured data is the foundation: This includes things like product specs, property details, course syllabi, etc., which usually come from a database.
- Supplement with unstructured/semi-structured content:
- Manual writing/editing: For high-quality content like core descriptions, reviews, and guides, manual intervention is still necessary.
- UGC (User-Generated Content): User reviews, Q&As, ratings, etc., are powerful tools for adding uniqueness and building trust.
- Aggregate third-party data: You can pull in weather information, map data, related news, etc.
- AI-assisted generation (use with caution): AI can help generate some descriptive text, but it must be manually reviewed and edited to avoid shallow or inaccurate content.
- Internal Linking Strategy: Plan the linking relationships between your pages, such as linking from list pages to detail pages and linking between related entities. This creates a web-like structure that's easy for both users and crawlers to navigate.
Team Collaboration is Key: This step requires close collaboration between product managers, SEOs, content strategists, and UI/UX designers.
Deliverable: Detailed page template wireframes or mockups, content field specifications, a content generation rulebook, and an internal linking strategy diagram.
A Hard-Learned Lesson: Cutting corners in the template design phase will lead to immense pain during content creation and optimization. Make sure you have a clear understanding of what information your users need and how to organize it for the best experience and conversion rates.
Step 4: Technical Selection and Development (Turning the Blueprint into Reality)
This is where you bring your design to life.
- Choose Your Tech Stack: Based on the project scale, your team's expertise, budget, etc., select the appropriate backend language (Python, PHP, Java, Node.js, etc.), database (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, etc.), and frontend framework (React, Vue, Angular, or a server-side rendering framework like Next.js or Nuxt.js).
- Develop Automation Scripts/Programs:
- Read from your keyword database and content sources.
- Dynamically generate HTML pages based on your templates and generation rules, or provide data to your frontend via an API.
- Handle URL generation and management (ensure clean, hierarchical URLs).
- Implement your internal linking logic.
- Implement Foundational Technical SEO:
- Performance optimization: Page speed is critical! Implement image compression, code minification/bundling, CDN acceleration, caching strategies, etc.
- Mobile-friendliness: Responsive design or a separate mobile site is a must.
- Structured data markup: Use Schema.org to help search engines understand your page content.
- Sitemap generation and submission: Automatically generate an XML sitemap and submit it to Google Search Console and other webmaster tools.
- Robots.txt configuration: Set up rules for web crawlers.
Team Collaboration is Key: The SEO team needs to provide the development team with clear technical requirements, and communication should be ongoing to ensure the final implementation aligns with SEO best practices.
Deliverable: A program or system that can automatically generate pages, and a frontend that is fully optimized for SEO.
Pro Tip: The technical implementation doesn't need to be overly complex. Stability, efficiency, and maintainability are key. Once you've decided on a URL structure, try not to change it.
Step 5: Launch, Monitor, and Continuously Optimize (The Final Step and a New Beginning)
Launching your programmatic SEO project is just the first step. Continuous monitoring and optimization are the keys to long-term success.
- Pre-Launch Checks: Ensure all pages are accessible, URL structures are correct, internal links are working, and core functionalities are operational.
- Submission and Indexing Monitoring: Submit your sitemap through Google Search Console and other webmaster tools, and closely monitor the indexing status of your core pages.
- Ranking and Traffic Monitoring: Use SEO and analytics tools (like Google Analytics, Ahrefs, etc.) to track keyword rankings, traffic sources, and user behavior.
- Collect User Feedback: Pay attention to user comments and customer service feedback to understand how real users perceive your pages.
- Data Analysis and Iterative Optimization:
- Analyze which pages/keywords are performing well and which are underperforming. What are the reasons?
- Based on data and user feedback, optimize your page templates, content quality, internal linking structure, user experience, etc.
- Regularly update your keyword database and content sources.
Deliverable: Regular project data reports and an ongoing optimization and iteration plan.
Personal Take: There's no "set it and forget it" in programmatic SEO. The market changes, user needs evolve, and search engine algorithms are constantly updated. Only through continuous monitoring, analysis, and optimization can you maintain your results.
5. Conclusion: The Rules of Survival for Programmatic SEO
Programmatic SEO is not just a "technical" or "manual labor" job. It requires you to:
- Understand users: Deeply understand what your target audience is searching for and what they need.
- Understand content: Be able to plan and organize valuable, differentiated content.
- Understand technology: Be able to choose and apply the right technical solutions efficiently.
- Understand data: Be able to identify problems and guide optimization through data analysis.
- Understand collaboration: Be able to facilitate close cooperation between content, product, and tech teams.
Final Piece of Advice: Don't always look for shortcuts or tricks. Put the user first, and use technology and content to create real value. That's the only way to build a sustainable and successful programmatic SEO strategy.
One last question: After reading this guide, what part of the process seems the most challenging to you? What strange pitfalls have you encountered in your own projects? Share in the comments and let's learn together!